Irregular Polygon Area Calculator
Calculate the area of any irregular polygon using coordinates and the Shoelace (Gauss) Formula. Supports negative values and unlimited sides.
| # | X | Y |
|---|
Finding the area of a shape sounds simple — until the shape stops being simple.
Once the sides are uneven, angles are different, or the outline bends in unexpected ways, most standard formulas stop working. You can’t just multiply length and width. And breaking the shape into smaller pieces often leads to mistakes or rough guesses.
That’s where an Irregular Polygon Area Calculator becomes useful.
Instead of forcing the shape into a formula, this calculator works the other way around.
You show it the shape — by drawing it, entering coordinates, or importing data — and it calculates the area from the actual outline.
No shortcuts. No assumptions. Just the exact area of the polygon you are working with.
What Is an Irregular Polygon Area Calculator?
An irregular polygon area calculator is a tool that calculates area based on the actual corners (vertices) of a shape.
Irregular polygons don’t follow a single pattern. Their sides and angles are different, so there is no one-line formula that works for all of them. The only reliable way to calculate their area is to use the coordinates of the vertices in order.
In simple terms, this calculator lets you:
- Draw the polygon point by point
- Enter or paste coordinate values
- Import existing measurement data
Once the shape is defined, the calculator uses a proven mathematical method to calculate the area precisely.
Three Easy Ways to Calculate Polygon Area
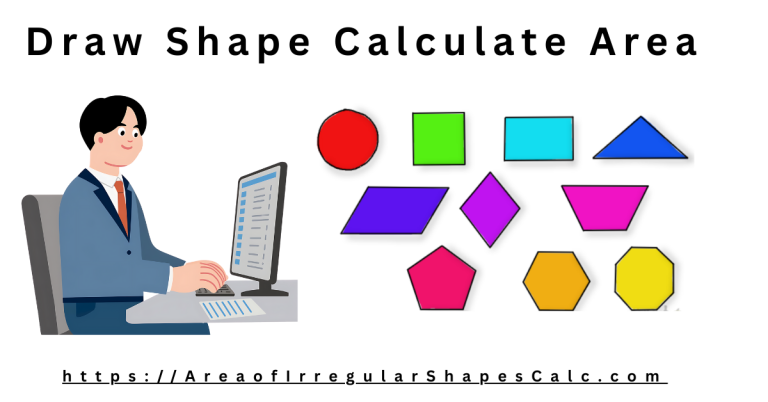
1) Draw the Polygon
This is the quickest option when you don’t already have coordinates.
- Click or tap on the canvas to place points
- Each point becomes a corner of the polygon
- Each edge shows its length in your selected unit
- Move points to adjust the shape
- The area updates instantly
You can see the shape, see the edges, and see the result at the same time — which makes errors easy to catch.
2) Enter or Paste Coordinates
If you already have data, this method is ideal.
- Enter points as ordered (x, y) values
- Paste coordinates from Excel, CSV, CAD, or GIS exports
- Supports decimals and negative values
This is commonly used for survey data, GPS points, and engineering drawings.
As long as the points follow the boundary in order, the calculator handles the rest.
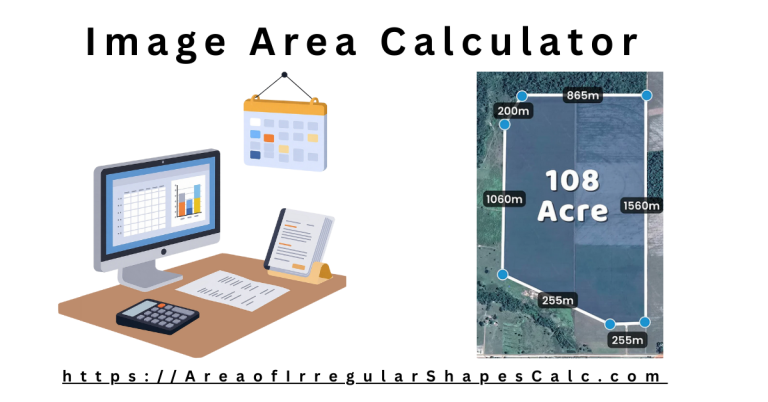
3) Import or Trace From an Image
If the shape exists only as a visual reference:
- Upload a map, floor plan, or sketch
- Set a known real-world distance for scale
- Trace the polygon boundary directly on the image
This approach works well when measurements are visible but not written as coordinates.
(For heavy image-based work, the dedicated Image Area Calculator may be a better fit.)
How the Shoelace (Gauss) Method Calculates Area
The calculator uses the Shoelace Formula, a trusted method used in surveying, mapping, and engineering.
You don’t need to memorize the formula, but it helps to understand the idea.
In simple terms, the method:
- Uses each vertex in order around the shape
- Combines the x and y values mathematically
- Calculates the area based on the full outline
Why this matters:
- It works for both convex and concave polygons
- The orientation of the shape doesn’t matter
- The result is exact for straight-edge polygons
This calculator does not hide the math.
You can see how the area is derived, which builds confidence in the result.
Units and Measurement Control
You can work in the units you actually need.
- Choose length units (mm, cm, m, ft, in)
- Choose area units (m², ft², acres, hectares)
- Each edge length is labeled directly on the polygon
Behind the scenes, all calculations are done consistently and then converted for display.
This avoids common mistakes caused by mixed units or rounding errors.
Where This Calculator Is Commonly Used
Irregular Rooms and Floor Plans
Measure rooms with alcoves, angled walls, or cut-outs that don’t fit rectangle formulas.
Land and Plot Boundaries
Paste survey coordinates or draw boundary points to calculate land area accurately.
Engineering and CAD Checks
Verify polygon areas from drawings or exported coordinate lists.
Learning and Problem Solving
Understand polygon area calculations clearly without guessing or skipping steps.
In all cases, the focus is the same: define the boundary, trust the result.
Common Mistakes — and How the Calculator Helps
Wrong point order
Points must follow the boundary. The calculator helps avoid self-intersecting shapes.
Too few points on angled edges
You can add more vertices for better accuracy.
Mixed units
Everything is standardized internally, so displayed units stay consistent.
Hidden calculations
Nothing is hidden. You can see what’s happening at every step.
Frequently Asked Questions
By defining its vertices in order and applying the shoelace method. This calculator does it automatically.
Yes. Points must follow the boundary, clockwise or counter-clockwise
Yes, as long as the edges do not cross.
Yes. Coordinate lists can be pasted or imported directly.
Yes. It is mathematically exact for straight-edge polygons.
Final Thoughts
Irregular polygons don’t need guesswork or complicated workarounds.
If you can define the corners — by drawing, typing, or importing data — you can calculate the area accurately. This calculator keeps the process clear, visible, and reliable from start to finish.